Cities (irrespective of their size) face different challenges related to globalisation, mobility, social and environmental change. Coping with them requires creative solutions, cross-sectoral cooperation and the involvement of citizens in decision-making processes. Moreover, with the active attitude of representatives of all urban stakeholder groups, cities have the opportunity to develop
based on diverse civic potential.
All these factors lead to a growing demand for a comprehensive tool to support city management. This tool is the urban lab.
What is the urban lab and who uses it?
At the Institute for Urban and Regional Development (IRMiR), we have developed the concept of urban lab as a response to the lack of an instrument in Polish cities to support cooperation between different groups of urban stakeholders, primarily between the city council and citizens. In the case of our concept, the initiator of activities and the institution managing the lab becomes the ‘city’ represented by the city council/municipality. This does not mean, however, that the urban lab instrument is reserved exclusively for the city authorities. Examples of labs created by, among others, universities, private corporations, partnerships or communities can be found in various countries around the world.
Urban lab is an instrument for building cooperation and dialogue between city authorities and citizens, NGOs, entrepreneurs and scientific bodies.
Its main objectives include creating harmonious cooperation for urban development and improving the quality of life of the inhabitants.
In other words, in the urban lab, i.e. a physical but also creative space, the interests of different groups of urban users meet:
- residents (active citizens, property owners, housing communities);
- non-governmental organisations;
- the public sector (municipal public institutions);
- the private sector (from start-ups to local micro-enterprises to global corporations);
- scientific entities (universities, research units, experts).
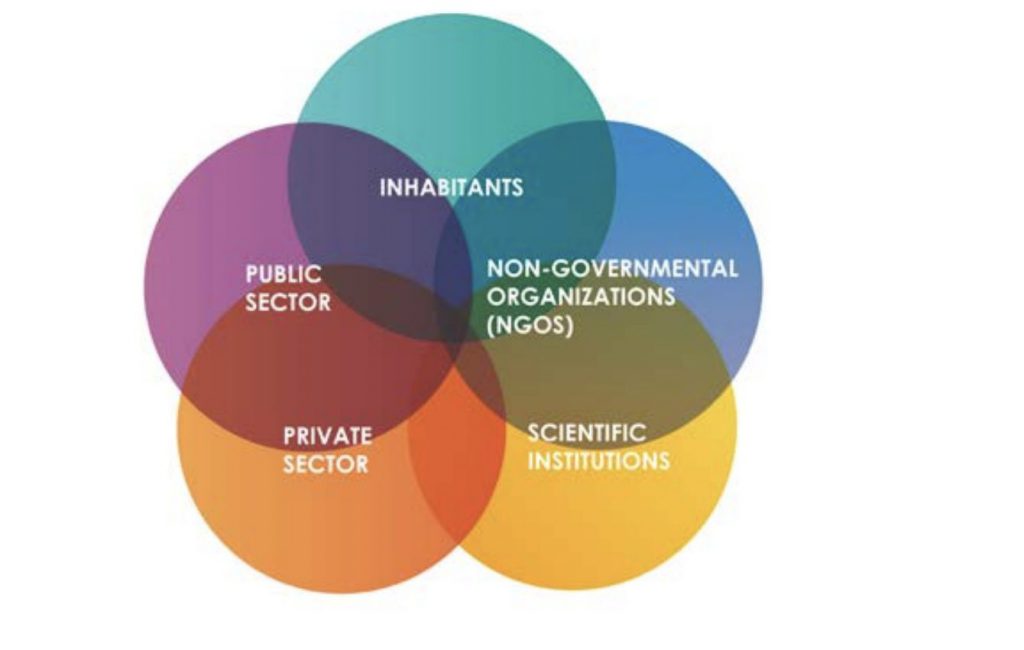
Each group offers its own unique potential which, in collaboration with the others, has the potential to be used to increase the momentum of collective action and develop the city’s creativity.
It is worth bearing in mind that the role and contribution of each stakeholder may vary from city to city, e.g. not in every city will the roles in urban lab be distributed proportionally – and that’s ok too 😊.
How does an urban lab work?
When conceptualising an urban lab, it is important to define the objectives, the thematic areas, the activities that the urban lab will carry out.
The scope of an urban lab can consist of a wide range of issues, among which we have modelled*: open urban data, urban innovation incubator, technological innovation, social innovation and urban space management (Fig.2).
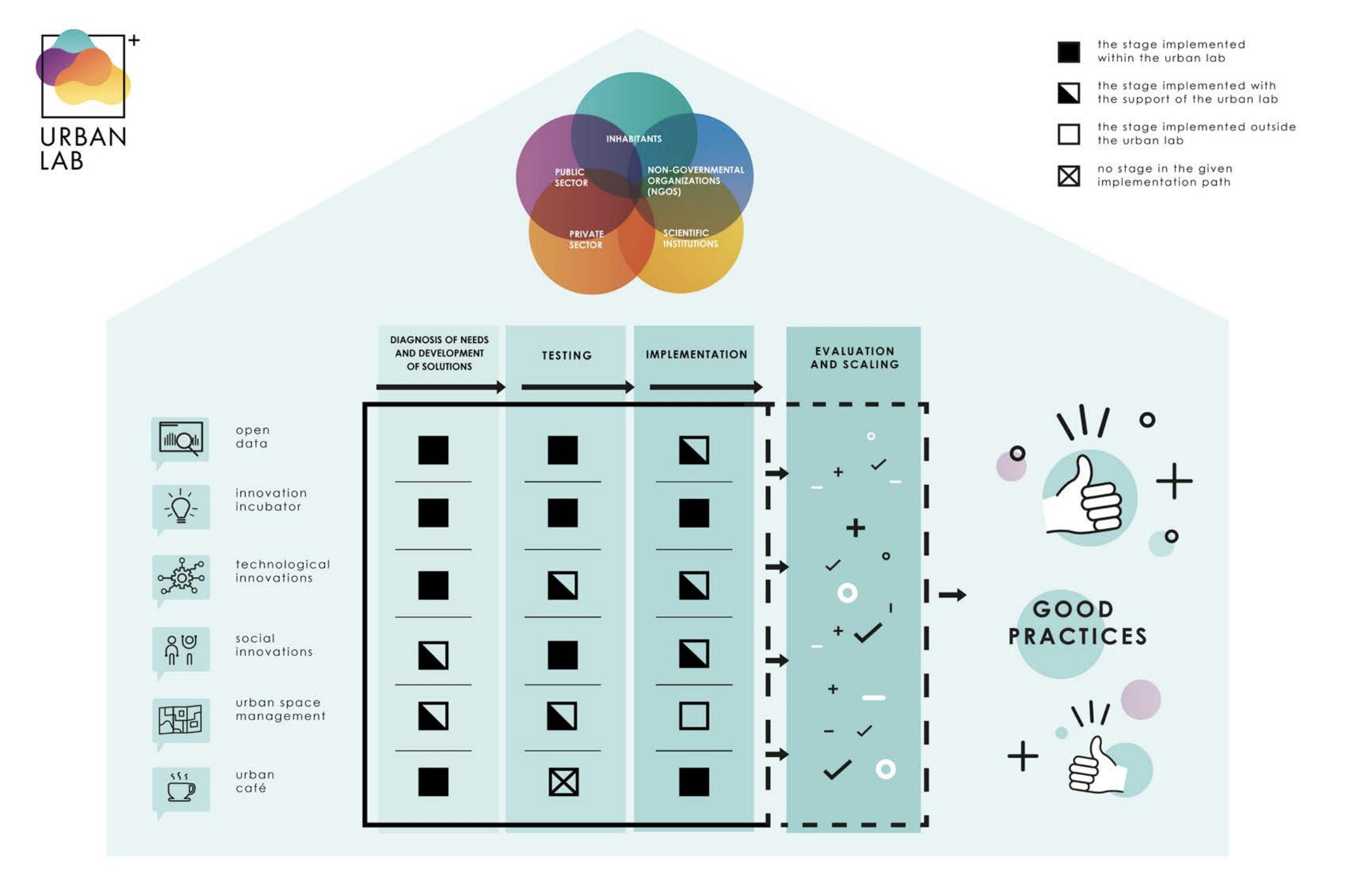
*The approach we present is MODEL, which means that the thematic areas and scopes of activities in each city can be completely different, ‘tailor-made’ for the city!
Each of the urban lab’s activities should go through the key stages of project implementation:
- diagnosis of needs and problems in the city / research into the needs of users (inhabitants),
- development of solutions,
- testing of developed solutions,
- implementation in the real environment,
- evaluation and possible scaling up.
It is worth noting that testing can be of a pilot character, on a limited scale (e.g. to one city district, at one intersection or in a selected park), in order to be able to find out about the effectiveness of a given solution or its shortcomings.
In an urban lab, all stages or only a selection of them can be implemented for the different types of activities undertaken. Some of them can already take place outside the lab, such as in the case of ideas that, after successful testing, are sent to commercial implementation by an entity interested in the solution.
The activities undertaken within the urban lab should each time be concluded with an assessment of their usefulness for a specific city in the form of an evaluation and the possibility of their application on a larger scale.
Urban Lab is also intended to be a place of inspiring meetings, a space for exchange of modern urban thinking, where numerous thematic events will be organised for citizens and with their participation, as well as with invited guests – experts in their field, from Poland and abroad, who will contribute with their knowledge to breaking stereotypes about the principles of city functioning.
We have therefore assumed that a conversation over a cup of coffee can become a contribution to a city-wide discussion. This is why the so-called urban cafe plays an important role in the model presented.
Urban Cafe as a fundamental activity of the urban lab
The urban cafe is a permanent activity for every urban lab – it functions all the time when the urban lab is operating. It serves to build and unite a community of people who care about creating a good and responsible urban future. It has a relaxed atmosphere conducive to Creative Creation.
The city is a place full of different voices to inspire and encourage action – go to the café to hear them. It’s a space where we talk or just listen to the hustle and bustle of the city – even in passing. And, of course, we drink good coffee:) This is precisely the idea behind the urban cafe.
One of the elements of Urban Cafe is a physical space open to everyone, adapted to people with disabilities, where you can have a good coffee and talk about the city, its potentials and problems, share ideas and propose solutions.
It is also a creative space, influencing the activation of the local community. It hosts events that are inspiring for residents, such as seminars, lectures, debates, training courses, conferences, workshops and film screenings. It is a place for less official meetings,
e.g. for members of social/non-governmental organisations or other groups of urban stakeholders.
Urban Cafe is not a café. The Urban Cafe is a new form of public participation and its formula should be adapted to the individual character of the urban lab in a given city.
To summarise:

As a result of the conceptual assumptions developed and the adaptation of the urban lab model to Polish conditions, a project entitled Urban Lab as a pilot tool for improving the quality of life of city dwellers in line with the smart city idea was implemented at the Institute for Urban Development and Regions in 2019-2021, which was financed by the Ministry of Funds and Regional Policy from the funds of the Technical Assistance Operational Programme 2014-2020. The project included the creation of urban labs in Gdynia and Rzeszów, which you can read about in our publication How We Made an Urban Lab. Conclusions and recommendations from the pilot implementation in Gdynia and Rzeszów (https://urbanlab.net/en/publikacja/how-we-made-the-urban-lab-conclusions-and-recommendations-from-the-pilot-implementation-in-gdynia-and-rzeszow/). Now, together with the MFiPR, we have launched the Urban Lab – City for the Young project financed by the Technical Assistance for European Funds 2021-2027.

